OVERVIEW
The Electrical Test Bench Demonstrator D19 focuses on the verification of the architecture and its associated technologies of an Electrical Power Generation and Distribution System (EPGDS) for Small Aircraft application, developed in the framework of Clean Sky’s work package 7 systems.
The activity kicked off in 2017, initially based on concept and trade studies. It aimed to demonstrate, in a dedicated test rig, the capacity and performance of a future system capable to generate and distribute electrical power in both high voltage and low voltage.
The demonstration has been performed in the ‘proven test bench’, a laboratory demonstrator based at Piaggio Aerospace, which was set up in collaboration with Thales and INDRA.

DESCRIPTION AND OBJECTIVES
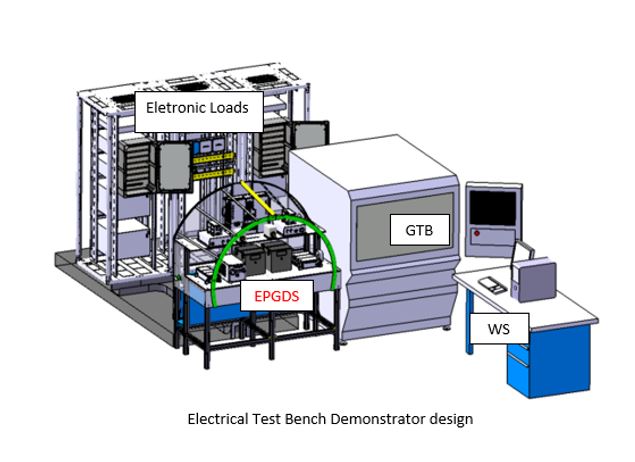
The Electrical Test Bench Demonstrator, designed and built by Piaggio, is composed by the following main sections:
- Electronic Loads;
- Ground Test Bench (GTB);
- Rig Control & Monitoring Workstation (WS)
and hosts the EPGDS composed by:
- Low Voltage Distribution Unit (INDRA)
- High Voltage Distribution Unit (INDRA)
- High Voltage Generation system (Thales)
- 28/270 DC-DC Converter unit (INDRA)
The Electrical Test Bench Demonstrator is able to implement the integration of the EPGDS components and verify their behaviour and performance under normal/abnormal (presence of failure) conditions.
Its aim is to demonstrate that the foreseen architecture and the technologies developed make the EPGDS suitable to supply and manage a large amount of electrical power to different typology of electrical loads, High Voltage (HV, 270 VDC) and Low Voltage (LV, 28VDC), increasing at the same time aircraft safety.
MAIN TECHNICAL ACHIEVEMENTS
The results of the verification accomplished by the Electrical Test Bench Demonstrator show that the EPGDS works properly when integrated in a representative environment consequently assess that the Technical Readiness Level 5 is reached.
The EPGDS developed offers the following improvements:
– Increase of the onboard electrical power with two generators for each engine
– Capability to supply a large typology of electrical loads with a dual voltage (28 VDC and 270 VDC) system
– Increase of aircraft safety with the management of multiple power sources (4 generators and two batteries)
– Improvement of reliability, maintainability and testability of the electrical system with the use of new technologies and diagnostic software
The main technological achievements are:
– A complex system architecture based on dissimilarity and redundancy
– New electrical components for power management and protection functions (e.g. SSPCs, S-Contactors…)
– New software for monitoring and diagnostic functions
– Weight and volume reduction